| CRITERIA | CONVENTIONAL IMPLANT | BASAL IMPLANTS |
| Shape and Structure |  | 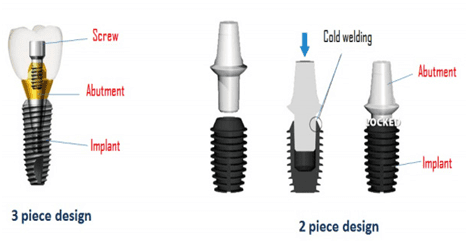 |
| Dental implant section | The screw are shaped with sandblasted/machined Hydroxyapatite coated dental implants surfaces. | Flat or blade like surfaces that has spaces which allows the bone to grow. |
| Bone requirement | The vertical bone - both the crestal & rarely just a small part of the basal bone. | This can be carried out in even resorbed bones or weak bone without doing bone grafting. |
| Bone displacement | A huge part of the bone substance is displaced or lost and may varies with size & length of implant. The crestal bone is more likely to resorption | Displaces less than 60% of the bone substance. Perfusion and Bone integrity are not likely to be impaired. The basal bone is very resistant to resorption |
| Technique | Insertion through the crestal bone is connected to the oral cavity more than it is connected to the basal implants. | You don’t need any cuts (Flapless), Insertion in the basal bone. The area that is bearing the load of implant does not have any connection with the oral cavity. |
| Cost of implant procedure | (a). Single implant cost ranges from INR 1799 and goes up to INR 50000
(b). Full mouth implant cost via conventional will cost INR 3l ac to 5 lac | (a). Single implant cost ranges from INR 1599 and goes up to INR 30000 depending upon brand you choose
(b). Full Mouth implant cost of installing of 18 implant comes to about 3,00,000 INR and can be done within 5 to 8 days while for a single arch may cost you about 1,50,000 INR within the same period |
| Bone grafting method | The essential in the cases of deficiency in the height of the bone. Grafting implants gives unpredictable results. | This is not necessary |
| Equipments used | Huge instruments set are necessary for this kind of procedures. | Instrumentation & skill are completely different & require extra training. |
| Gums penetration diameter | Chances of peri implantitis, vertical bone loss, are greater,crater like bone loss & infections are slightly high | Smaller (just 1.9mm - 2.3mm). The whole part of the vertical implant is polished - hence, odds of problems being seen as it is in the case of crestal implants very low. |
| Anatomy – closeness to Inferior Alveolar Nerve and the Maxillary Sinus | Very imperative consideration & technique has to be altered accordingly. Bone augmentation is necessary in most cases. | Doing away with unfavorably placed Inferior Alveolar Nerve and Maxillary Sinus is possible |
| Abutment angulations | 2 piece implants ought to have the pre-angulated abutments. KOS piece implants give bendable abutment as well as angulated provisions. | All of this kind of Implants have bendable abutments. |
| How it is loaded | Prosthesis is loaded within 3 days of implant surgery thus saving on time & costs considerably. In the case of conventional implants associated with grafting procedures/ bone augmentation, the whole treatment period will be about half a year to a year. The requirement for interim provisionals/ dentures is totally eliminated | It is Loaded immediately, no waiting time to get teeth - all patients get fixed teeth in 3 days. |
| Masticatory forces | Act in the vertical direction along the sides of the screw structure | Transferred to the basal plate deep into the cortical bone areas which are able to accept large loads and have great capacity for regeneration. |
| The Bone-Implant Relationship | most of these implants take support from the basal bone which is a lot more resistant to resorption, very much unlike the conventional implants which mostly take support from the crestal bone. Basal cortical bone also has a much faster and stable repairing capacity | The implant selected for the site can be modified to suit the available bone height and width |
| Applications in destructive periodontitis & after multiple extractions of teeth | Placement nearly impossible and success is unpredictable. | Placement of implants very much possible and results are excellent. |
| Smoking patients | Smoking habit affect the implant procedure negatively because it cuts down the blood flow to the oral tissue like the gums, teeth and bone, which in turn results in slower healing of the implant site. Smokers have a high risk of gingivitis and gingival recession which in turn will lead to infection around the implant (peri-implantitis) leading to their failure. In case of basal implants, since the load bearing areas are far away from the areas of the mouth affected by smoking, they take up well. However, it should be borne in mind that smoking immediately after implant surgery will be unfavorable for wound healing even in the case of basal implants. | Best option for smoking patients |
| Controlled diabetic patients | The conventional dental implants are generally contraindicated in diabetes patients, since diabetes is associated with increased susceptibility to infection, impaired wound healing and gum diseases (gingivitis, periodontitis, etc.) However, basal implants work absolutely well in controlled diabetic patients because they are smooth surface implants which do not permit bacterial colonization on the implant surfaces | Blood sugar variations may not affect the survival of the implant at all. |